TL;DR: February’s Go Flux Yourself examines AI’s failure of women and girls, from deepfakes and biased recruitment tools to the structural exclusion of female voices from the systems being built. It asks why the human skills the AI age demands most are the ones we’ve spent decades undervaluing.

Image created by Midjourney
The future
“There are billions of dollars being invested globally in the belief that AI represents a brilliant new future, which must be pursued at all costs. At present, for women and girls, that promise is a lie.”
These words come from Laura Bates, founder of the Everyday Sexism Project and author of The New Age of Sexism, writing in the Financial Times. I read her essay last Saturday morning over a cup of fresh-cut lemon and ginger tea, and the superb piece soured my weekend. It landed, by chance or perhaps editorial design, a fortnight before International Women’s Day (Sunday 8 March), whose 2026 theme is “Give To Gain“, the idea being that when people, organisations, and communities invest in women, the returns are shared. When women thrive, we all rise.
That sounds hopeful. But it rings hollow without confronting what artificial intelligence is actually doing to women and girls right now. And this month’s Go Flux Yourself is written squarely with them in mind.
The details, listed in Bates’s article, are grim. In late December, xAI’s Grok tool was used to generate millions of non-consensual intimate images of women over just nine days. Requests to add bruises, blood, and bullet holes to women’s photos were instantly granted. So-called “nudify” apps have been downloaded more than 700 million times worldwide, generating $117 million in revenue, with Apple and Google taking a cut. When Elon Musk’s company was confronted with the outcry, it didn’t disable the feature. It restricted it to paying subscribers, monetising the abuse instead of stopping it.
But Bates’s argument goes deeper than deepfakes. Research published last August by the London School of Economics found that AI tools already used by more than half of England’s councils were downplaying women’s medical conditions. Meanwhile, a 2025 German study found that ChatGPT consistently advised women to ask for lower salaries than men, even when both had identical qualifications – in one case, a disparity of more than $100,000. And a University of Melbourne study found that 42% of global companies are already using predictive AI systems in recruitment, despite repeated expert warnings that such tools may actively discriminate against female applicants, as well as candidates wearing headscarves and those with “Black-sounding names”.
According to UNESCO, women globally make up just 12% of AI researchers and 6% of software developers. Additionally, female founders receive only 2.3% of venture capital funding. As Bates puts it: “We are not the ones building this new world. But we will have no choice about living in it”.
These are not edge cases or teething problems. They are the architecture of a system designed largely without women’s input, now being deployed at scale. It’s as though someone built a city, forgot to consult half the population, and is now surprised that the buildings don’t have doors the right size.
At the precise moment AI is amplifying old patterns of gendered power, the skills the AI age demands most – curiosity, empathy, critical thinking, collaboration – are the ones that women have been practising in leadership for decades, usually without much credit. The evidence shows they produce results. And yet inclusion programmes are being scaled back, entry-level roles are vanishing, and the old metrics still reward the loudest voice in the room. We’ve discovered the antidote to the disease, and we’re pouring it down the drain.
For these reasons, it’s worth listening carefully to the people building the technology itself. Daniela Amodei, co-founder and president of Anthropic, the company behind Claude, one of the most powerful AI systems in the world, put it smartly in an interview with ABC News earlier this month. Amodei studied literature at university. Not computer science. Not mathematics. Literature. She now runs a company at the frontier of a technology that could reshape every industry on the planet. And her message to young people entering the workforce? Learn to communicate. Develop emotional intelligence. Be curious and compassionate.
“I actually think studying the humanities is going to be more important than ever,” she said. “The things that make us human will become much more important instead of much less important”.
Even JPMorgan’s Jamie Dimon, not a man known for sentimentality, told an audience in December that young people should focus on communication and critical thinking. Get those right, he said, and “you’ll have plenty of jobs”. When the head of the world’s largest bank starts sounding like a humanities professor, something significant is happening.
The message from the top of the technology industry is clear: human skills are the future. So why aren’t we investing in the people who’ve been practising them longest?
Helen Wada spent 12 years at KPMG, rising to Global Client Leader. She’s a chartered accountant, an executive coach, and the founder of The Human Advantage. Her book, HUMAN-WISE: How to lead from within and sell with confidence, is published next week, on 3 March, just a handful of days before International Women’s Day. The timing is not coincidental.
When I spoke to her, she told me about a client meeting she’d coached recently. A team had spent months cultivating a business relationship, carefully building trust and rapport. They were close to converting. Then a senior leader who hadn’t been involved was brought in. His approach? “We’ve done two pre-sales meetings. Let’s go in for the kill.” He destroyed what they’d built. Because his metrics rewarded speed and aggression, not the patient work that had created the opportunity in the first place.
That anecdote, Helen says, is the problem in miniature. Performance is still measured through individual targets and personal visibility, with little recognition for collaboration or shared success. Women face a persistent double bind. Lead with empathy, and you’re seen as lacking commercial edge. Step into more direct territory and the language shifts: “too assertive”, “too challenging”, “not quite the right fit”.
“The behaviours are rarely the issue,” she said. “It’s the interpretation that holds people back”.
Helen’s argument – and it’s a compelling one – is that the familiar question should be flipped entirely. Instead of asking how women can lead more like men, we should ask how men can lead more like women: by bringing curiosity, collaboration, and coaching to every conversation. The companies that do this outperform. The ones that don’t keep wondering why their culture feels like it’s running on fumes.
McKinsey’s 2023 research found that companies in the top quartile for gender diversity are around 27% more likely to outperform their peers financially – a statistic so well-worn it’s practically wallpaper. Yet, the gap between knowing and doing remains vast.
The talent pipeline, meanwhile, is cracking. Graduate jobs in the UK have fallen by roughly two-thirds in the past three years. If you remove the first rung of a ladder, it doesn’t matter how progressive the penthouse is: nobody can reach it.
Heather Delaney, the American-born founder of London-based tech communications firm Gallium Ventures, where the majority of staff are women, has been watching this trend closely. She built and scaled Dynamo from a three-person team to a global agency before leaving what she describes as a toxic environment. Now she hires deliberately from non-traditional backgrounds, including through apprenticeship schemes.
“Some of the best employees I’ve hired lack degrees but are hungry and curious,” she told me. “Those traits can’t be taught. What I look for is the ability to ask questions.”
What worries Heather most is that AI threatens the junior roles that produce future leaders. “If AI handles research and entry-level tasks, those roles may disappear entirely. That denies future leaders their start.” The industry, she predicts, will swing hard into AI and then correct back towards the human. “Ideas, personal contacts, and relationships are indispensable.” But the correction won’t help if a generation of talent has already been lost. You can’t replant a forest that’s been clear-cut and expect shade by lunchtime.
Anna Vignoles, director of the Leverhulme Trust and a leading education researcher, sees the challenge from the other end of the telescope. I spoke to her shortly after her first visit to the World Economic Forum in Davos in mid-January, where she’d appeared on a panel chaired by William Hague called “Defying Cognitive Atrophy“, exploring how AI could strengthen or erode human thinking. The session examined the overarching paradox that sits at the heart of this newsletter: cognitive skills are becoming more economically valuable, yet humans are outsourcing more of those functions than ever.
“We’re up against evolutionary biology,” Anna told the Davos audience. “All species like to conserve energy. Humans are no different. Learning takes effort. When you’re an adult, outsourcing your cognitive thinking might be fine. But as a child, if you don’t get the chance to develop those cognitive skills, to develop those neural pathways, we’re in trouble.”
On the global picture, she was sobering. “There are still 120 million girls not in education. Predominantly in low-income countries. That remains one of the most significant problems we face.”
In developed countries, the picture is more nuanced. While women’s participation and achievement in higher education have increased substantially, a reverse trend has emerged: boys, particularly from low-income backgrounds, are underachieving across multiple stages of the education system.
AI, Anna argues, risks widening both gaps. “The impact depends entirely on the user’s experience level,” she told me. “For experienced professionals, it’s a useful tool. For new entrants, reliance on AI could prevent them from mastering foundational job skills. You need clever, informed, experienced humans in the loop, and if AI cuts off the pipeline that produces them, we have a serious problem.”
She’s particularly worried about equity. AI tutors will be commercialised. Access will depend on the ability to pay. Large corporations will build bespoke systems. SMEs will be stuck with whatever comes out of the box. That gap will compound everything else. And as she pointed out at Davos: “You only get one shot at being five-years old. What we might do in business about a difficult transition can’t necessarily apply to the school system.”
Her advice for parents, though, was reassuringly old-fashioned: read widely, develop critical thinking, and understand data and statistics. The challenge is convincing children that these foundations matter when AI seems to offer them a shortcut. Trying to persuade a teenager to build their own sandcastle when a machine can produce a replica palace in seconds is, to put it mildly, a hard sell.
The pattern across these conversations matters for International Women’s Day. The AI age demands human skills. Human skills have been systematically undervalued. The people who’ve been developing them – often women, often in roles that don’t attract the flashiest titles – are exactly the people organisations need most. And yet the technology itself actively encodes the biases that held women back in the first place.
But smart women are already making smart decisions. Amodei, a literature graduate, runs one of the most consequential AI companies on the planet – not despite her humanities background, but because of it. Helen is reframing what leadership looks like, arguing that the qualities dismissed as “soft” produce hard commercial results. Heather and Anna, from opposite ends of the talent pipeline, are both insisting that curiosity and access matter more than credentials and postcode. These are not women waiting for permission.
The 2026 IWD theme is Give To Gain, as mentioned at the top of this piece. The premise is that when we invest in women – through mentoring, education, resources, and visibility – the returns are shared. Giving isn’t subtraction. It’s multiplication.
The challenge for the rest of us, and for every organisation claiming to take AI seriously, is whether we’re prepared to give generously enough to gain what genuinely matters. Or whether we’ll keep measuring what’s easy to count and ignoring what keeps the whole thing standing.
The present
Last weekend, the Baftas took place at London’s Royal Festival Hall. The headlines were dominated by John Davidson, the Tourette syndrome campaigner whose life inspired the film I Swear, involuntarily shouting a racial slur while Michael B. Jordan and Delroy Lindo were presenting onstage. The BBC, broadcasting on a two-hour delay, failed to edit it out. That story will run and run, probably until more people at the BBC are forced to resign.
But it overshadowed something I think is more significant, which I picked up from the FT’s coverage ahead of the event. Bafta chair Sara Putt told the paper that her organisation has introduced “human creativity” as an explicit criterion for its awards. AI-generated performances are now banned from acting categories. The London-based Mise En Scène Company has gone further, labelling all its film titles “No AI Used” and calling for a certification system comparable to fair trade or organic labelling.

Image created by Nano Banana
When one of the most established institutions in British culture feels the need to specify that its awards celebrate human achievement, something fundamental has shifted. (And the person making that bold call is a woman.) Putt looked at the encroachment of generative AI into creative industries and drew a line. That takes judgment and nerve. It also raises a question worth asking across every sector: should other industries introduce their own version of a “human creativity” standard? What would it look like in consulting, in journalism, in education? The smartest decisions being made about AI right now – where to draw boundaries, what to protect – are disproportionately being made by women. Not exclusively. But the pattern across this edition is hard to ignore.
Meanwhile, Hull-hewn Robert Aramayo’s best actor win for I Swear, beating Hollywood stars Leonardo DiCaprio and Timothée Chalamet, was itself a quiet triumph of human storytelling over star power. Sometimes the most powerful films are the ones that make you uncomfortable.
Away from cinematic glitz, every Friday morning for the past month, I’ve been filming myself talking unscripted, for around three minutes, about whatever I’ve seen, heard, and thought about that week regarding human-work evolution. I call it Thank Flux it’s Friday, and it’s making the most of an “AI slopportunity”. Certainly, in a world where an estimated 90% of online content is now AI-generated, there’s a premium on content that is visibly, unmistakably human. And TFIF is a work in progress, for sure. (You can see the (slow) progression of rawness and production values here, on my new Go Flux Yourself YouTube channel.)
Earlier this month, I was at The RSA for The Observer‘s event on AI, hosted by James Harding and featuring its new Global AI Index. Only 35% of people in the UK use AI, the index found, ranking the country 15th (despite being fourth overall) in implementation “due to lower public acceptance”. Is that reluctance, or discernment? Maybe both.
Next week I’ll be in Paris for a pharmaceutical company, recording stories and moderating a podcast with their scientists. Every person I’m speaking to could have taken a more lucrative position at a big tech firm. They chose instead to focus on saving lives. It harks back to what Rutger Bregman described in November’s Go Flux Yourself as the “Bermuda Triangle of Talent”: the way consultancy, finance, and law firms hoover up brilliant minds who entered university wanting to cure diseases, and redirect them towards helping people click ads. The scientists in Paris climbed the ladder that was worth climbing. They have the “moral ambition” that the Dutch historian says we should all strive for.
Looking ahead, I’m in discussions to speak at both SXSW London and London Tech Week in June. I’ve also been invited to deliver a keynote for a major telecoms company during London Tech Week, examining why faster networks don’t seem to foster deeper human connections.
If the IWD theme is Give To Gain, consider this an open invitation. I’m always looking for interviews, case studies, and examples of organisations genuinely investing in human capability alongside AI adoption. Send them my way: oliver@pickup.media.
The past
Four years ago, on 24 February, Russian tanks rolled into Ukraine. Vladimir Putin expected Kyiv to fall within days. Soldiers reportedly packed parade uniforms. They didn’t need them. There’s no sign they’ll need them anytime soon.
What has happened since constitutes the most significant real-world laboratory for AI that has ever existed. And it tells us something profoundly uncomfortable about where AI is headed, in the workplace and beyond.
When we talk about AI at work, we tend to discuss chatbots and productivity tools, quarterly earnings calls and Big Four reports. But the starkest test of AI’s capabilities isn’t happening in a Silicon Valley campus or a London boardroom. It’s happening in the mud and rubble of eastern Ukraine, where drones now account for roughly 70-80% of all of Russia’s battlefield casualties.

Image created by Nano Banana
The numbers are staggering. Ukraine produced around 800,000 drones in 2023. By 2024, that figure hit two million. In 2025, production reached at least four million. Russia established its own Unmanned Systems Forces in November 2025, mirroring Ukraine’s earlier move to create the world’s first dedicated military drone unit.
But the truly unsettling part isn’t the volume. It’s the intelligence. Ukrainian forces have taken publicly available AI models, retrained them on classified real-world battlefield data, and deployed them on drones that can autonomously fly the final 100 to 1,000 metres to their targets. According to research by Kateryna Bondar at CSIS, this AI-enabled autonomous navigation raises strike success rates from around 10-20% with manual control to 70-80%. That isn’t an incremental improvement. It’s a transformation.
Bondar, a Ukrainian-American scholar, former adviser to Kyiv’s government, and a fellow at CSIS’s Wadhwani AI Center, told Breaking Defense that while fewer than 0.5% of Ukraine’s drones had AI guidance in 2024, the military aimed for 50% in 2025. If realised, that would mean roughly a million AI-assisted drones, each three or four times more likely to hit their target.
The innovation cycle is another thing altogether. In 2022, new battlefield technologies lasted about seven months before being superseded. By early 2025, that cycle had collapsed to just four to six weeks. Samuel Bendett, a senior fellow at the Center for a New American Security, observed that three years of war had generated “centuries’ worth of data” from air, space, ground, and cyber sources. That data is now training the next generation of autonomous systems.
As Austrian Foreign Minister Alexander Schallenberg warned at a Vienna conference on autonomous weapons, this is the “Oppenheimer moment of our generation”.
In 2017, the Future of Life Institute and Berkeley professor Stuart Russell released a short film called Slaughterbots. It depicted a near future in which palm-sized autonomous drones used facial recognition to shape explosives and assassinate targets. A tech executive pitches that nuclear weapons are now “obsolete”: a $25-million order of drones can kill half a city. The film was screened at a United Nations convention on autonomous weapons in Geneva that same month. I remember watching it nine years ago and finding it alarming. But it feels like we are already reaching the “futuristic” capabilities warned about via this dark eight-minute video less than a decade ago.
Earlier this month, CNN reported that Russia has begun deploying drones with motion sensors that fly into the battlefield, wait for infantry to pass, and then detonate. Imagine that: a machine, hovering silently in a trench or a ruined building, making a decision to kill based on movement. No human finger on the trigger. The technology Russia is deploying in Ukraine is uncomfortably close to the scenario Russell warned us about. The open question is not whether this technology exists. It’s whether it’s in the right hands, on and away from the battlefield. And on current evidence, the answer to that should keep all of us awake at night.
With it being International Women’s Day next Sunday, consider this: some of the most consequential figures in this AI revolution are women. Bondar’s research at CSIS has become essential reading for Western defence strategists.
Kateryna Chernohorenko, a lawyer by training, became Ukraine’s Deputy Defence Minister for Digital Development and initiated the “Army of Drones” project that fundamentally changed how the country fights. She led the Drone Coalition – attracting 18 partner nations and raising €2.2 billion – and integrated the Avengers AI platform into battlefield surveillance, enabling automated detection of enemy equipment from drone footage in roughly two seconds.
Lyuba Shipovich runs Dignitas Ukraine, a volunteer-driven nonprofit that provides technology support to the Ukrainian army. Kateryna Bezsudna leads a defence tech startup accelerator where products must be operational within six months, the average window before Russia introduces a new weapon.
And on the front lines, technology has opened doors that were firmly shut. More than 70,000 women served in Ukraine’s military in 2025, a 20% increase since 2022. Drone piloting has become one of the most popular combat roles for women. A soldier known as Yaha joined the army in 2023 and was told by commanders to replace the cook when she asked about drone training. She spent her kitchen shifts studying manuals and practising on a simulator she bought herself. She’s now a bomber-drone pilot in the 9th Brigade. As she told the Associated Press: “I liked that you could strike the enemy remotely. So I thought this was our future”.
She’s right, it is. But are we prepared for it? Nobody’s life depends on whether your marketing team adopts AI properly. But the underlying dynamics are identical: the speed of technological change outpacing human adaptation, the ethical questions we’re failing to answer, the gap between those building the tools and those creating the governance, and the stubborn institutional resistance to letting talented people do what they’re capable of, regardless of who they are.
Ukraine is producing a generation of technologists battle-tested in ways no corporate innovation lab could replicate. When this war eventually ends, tens of thousands of people – men and women – will carry expertise in AI, robotics, electronic warfare, and rapid-cycle innovation into civilian life. The countries and companies smart enough to learn from them will have an extraordinary advantage. As Oleksandra Ustinova, a Ukrainian member of parliament, put it bluntly: “If your drone hasn’t been tested in Ukraine, it’s still just a toy”.
We owe it to the people fighting – and dying – in this conflict to take the implications seriously. Not just for defence policy, but for how we govern AI, how we invest in human capability alongside technological capability, and how we ensure that the people driving these transformations aren’t sidelined because they happen to be women, or young, or from a country that doesn’t make the front pages any longer.
Four years on, Ukraine hasn’t fallen. But the world it’s fighting in has changed beyond recognition. And so has ours.
Tech for good: Luca Health and saving rugby from itself
The Six Nations rugby tournament is back, and with it the annual ritual of grown adults screaming at a television as though tactical advice delivered at volume might somehow reach the coaching staff. England’s men head to Rome and then Paris in March. The Women’s Six Nations kicks off in April, with the Red Roses defending a crown that now includes both the Six Nations title and last summer’s Rugby World Cup. That World Cup triumph capped a remarkable summer period for English women’s sport: Sarina Wiegman’s Lionesses won the 2022 and 2025 European Championships and reached the 2023 World Cup final, making them arguably the most successful English team – male or female – in sporting history.
Rugby is very much in our household right now. My son Freddie, who is 11 and rugby mad, has just been offered a place at a secondary school with a strong rugby programme and links to several London clubs. His current ambition is to become a professional rugby player. The school may have other ideas – it seems rather keen on well-rounding its students – but for now, weekends revolve around matches, bruises, and the kind of post-game mud that no washing machine was designed to handle.
But being the parent of a young rugby player means you live with a low-level hum of anxiety that never entirely switches off: concussion. It’s the word that hangs over the sport like a weather front. More than a thousand former professional players are suing the RFU and World Rugby. Former internationals – heroes to children like Freddie – are being diagnosed with early-onset dementia in their forties and fifties. World Cup winners can’t recall details of the biggest game of their lives. Some have publicly said they love the game but wouldn’t let their own children play it.
Which is why this month’s tech for good story matters. Nick Greenhalgh came through the academy at Northampton Saints alongside Courtney Lawes, now an investor in his business. Nick gained a professional contract, but injuries ended his playing career early. He walked away, completed an MBA, and spent six years in tech before founding Luca Health, a concussion management platform for grassroots sport.
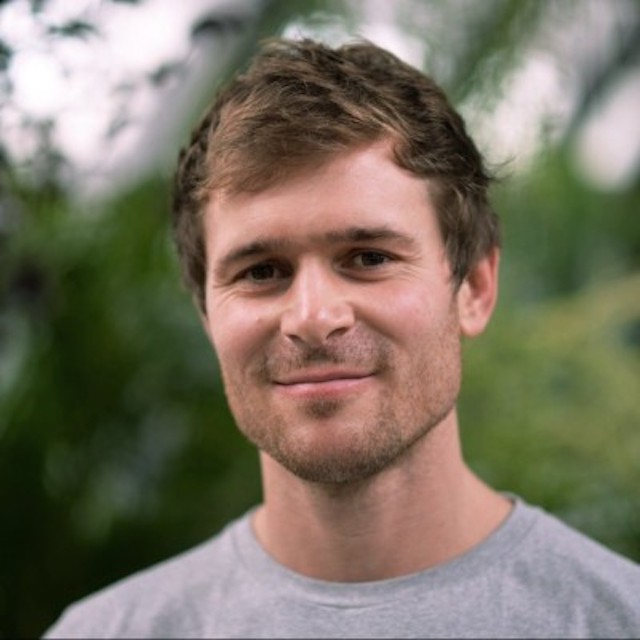

Nick of Luca Health
The problem Luca solves is deceptively simple and alarmingly widespread. When a child takes a knock to the head at a school match or a Sunday morning club game, what happens next? The school nurse isn’t qualified to diagnose a concussion. The local GP probably isn’t familiar with the latest protocols either. A&E will filter for traumatic brain injury (bleeds, swelling) and send a concussed child home with a leaflet. In most grassroots settings, there is no specialist in the loop. No system. No follow-up.
Luca fills that gap. Schools and clubs get a dashboard showing every player: who’s on a return-to-play protocol, who isn’t, and what stage they’re at. Within each child’s profile, you can see incident history, clinical notes from telehealth consultations, symptom reports, and objective test data from the Luca app. Players complete a baseline battery on their phones: memory exercises, reaction-time games, spatial reasoning, plus eye-tracking and pupil-constriction tests that use the smartphone camera and AI to measure what was previously possible only with specialist hardware. After an incident, follow-up tests are compared against that baseline.
There’s no single test that definitively confirms a concussion; it remains an inherently subjective diagnosis. But Luca is making it as data-driven and objective as the science currently allows. Teachers are notified about classroom allowances. Parents can log in and see where their child is on the protocol. Coaches can log incidents in real time. It’s the kind of infrastructure that should exist everywhere but simply doesn’t.
Nick was put on to me by the journalist Sam Peters, author of Concussion, who has done more than almost anyone to drag this issue into the light. Courtney Lawes and Alex Waller – holder of the Premiership appearance record – are both investors. Luca is currently working with 10 schools and clubs and plans to reach 25 by September. Nick’s two-year ambition? To work with governing bodies so that anyone playing community rugby or hockey in this country has access to specialist concussion support. State schools remain the challenge: the economics of volunteer-led clubs and underfunded state sport make scaling difficult, and corporate sponsorship may be the answer.
I asked Nick what keeps him going. His answer was simple: confidence. Not for himself, but for parents. “We want parents to feel confident that if their kid takes a knock, there’s a proper system in place. Because without that confidence, they’ll pull their kids out. And then the sport dies.”
Here we have technology supporting human judgment rather than replacing it, and protecting young heads rather than optimising for profit. With Freddie lacing up his boots every weekend, it couldn’t feel more personal.
Statistics of the month
🎭 Pretending to be fine
Nearly seven in ten UK employees now admit to pretending to be well at work when they’re not – up from 51% in 2021. Money worries (49%), a lack of understanding from management (26%), and health stigma (19%) are the main reasons. The cost of this “pleasanteeism”? An estimated £21 billion in lost output annually. (Lime Health / Censuswide)
💰 Finance stress is costing us
Some 83% of UK workers say they’ve taken time off in the past year due to stress, anxiety, or illness linked to personal finance concerns. Employees spend an average of 2.24 hours per month handling personal finances while on the clock. (Stream)
🤖 The scam ad epidemic
Nearly one in three Meta ads running in the EU and UK over a 23-day analysis period were scams, based on a study of 14.5 million ads and 10.7 billion impressions. More than half of those scam ads were driven by just 10 advertisers, pointing to coordinated, industrial-scale operations. (Gen / Norton)
🧒 Banning won’t fix it
While 78% of UK adults support banning under-16s from social media, most expect young users to bypass restrictions: 75% say children would lie about their age or use fake accounts, and 67% believe a ban could push young people towards more dangerous, less moderated online spaces. (Harris Poll UK)
📉 Youth unemployment bites
UK unemployment hit 5.2% in February, the highest in almost five years. Among 16 to 24-year-olds, 16.1% don’t have a job, the weakest figure in over a decade. For a generation told that education was the route to opportunity, the landing zone looks increasingly barren. (ONS)
If you’re reading this and haven’t yet subscribed, you can sign up for Go Flux Yourself (there should be a pop-up). Each edition lands on the last day of the month.
Get in touch: oliver@pickup.media. I write, speak, and strategise on the future of work, AI, and human capability. For speaking enquiries, contact Pomona Partners.